Excerpt from the Speech of the Head of State
I instructed the Government to accelerate the establishment of the preconditions for the industrialization of our country. These essential conditions are:
the development of communication and telecommunications infrastructure.
In this last area, we must catch up as quickly as possible with our delay in the development of the Digital Economy. This is a real growth accelerator, in addition to being a real niche of new jobs for our youth. We must be able to take full advantage of it. The Government, in its organization, will give this sector all the attention it deserves.[…]
Extract from the Message of the Head of State to the Nation
on the occasion of the end of the year 2015 and the New Year 2016
The Knowledge and Knowledge Society has created the changes in
human needs as well as the way to address and satisfy them. This has been favored by the development of new technologies and electronics which have refined the
industrial revolution that took place almost two centuries ago today. Physical and virtual goods
coexist, distance is no longer an obstacle
for the instantaneous action.
This new paradigm of the 21st
century has taken on the term “all digital”.
In this global context marked by the transformation towards “all digital”, Cameroon has undertaken major projects on the
institutional, regulatory and infrastructural levels that should lead
to digital emergence by 2035. The Head of State,
His Excellency Paul Biya has set the course in his vision for the
continuation of these projects, prerequisites and essential conditions
for a real industrialization of our country.
Despite the size of the investments made to date, the level
of use of Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) by local populations and businesses remains
very limited. By way of illustration, Internet access at home still remains at 12.3% in urban areas and 1.4% in rural areas*.
Similarly, the popularization, dissemination, adoption and appropriation of ICTs in Cameroon remain insufficient.
Based on this observation, the President of the Republic, His Excellency
Paul Biya, in his end-of-year address to the nation on December 31, 2015, forcefully affirmed that “…we must catch up as quickly as possible in the development of the Digital Economy. This is a real growth accelerator, in addition to being a real niche of new jobs for young people”.
The concept of digital economy translates new models of exchange and sharing of information based on ICT, creation of wealth and
which modify almost all the modes of production of goods
and services of other sectors of the economy. activity.
The digital economy has three pillars. The first, referred to as
the heart of the digital economy, is based on the development of
broadband electronic communications infrastructure and
the computing and electronics sectors, while the
second and third relate respectively to activities arising
from fact of the development of ICT and the transformation of
existing sectors of activity, by integrating the use of ICT.
Indeed, ICTs impact on growth and employment on the one hand,
through their intrinsic contribution to the economy, the generation of direct and indirect jobs and the popularization of job offers in
the Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020
PREAMBLE
the real economy and by the induced effects of their introduction into
the production process of all branches of
economic activity, thus improving their productivity, their competitiveness and innovation, leading to a substantial increase in
GDP on the other hand.
Here is therefore a compass that highlights the actions to be carried out and proposes appropriate measures for the development of ICT uses and content as well as the implementation
of accompanying policies relating thereto for the emergence of the digital economy in Cameroon.
Developed in synergy with all stakeholders, the
“Digital Cameroon 2020” strategic plan, which is in
line with the implementation of the “Great Achievements” policy advocated by the Head of State, should contribute greatly to the achievement of the growth and full employment objectives targeted by the Government over the next five years, through more intensive use of ICT in production tools, resulting in a substantial improvement in
national productivity.
This developed plan is based on three main pillars relating respectively to aspects related to supply, demand,
regulation and governance. Throughout its implementation programmed over five years (2016-2020), the Government will pay the greatest attention to the following priorities:
– developing broadband infrastructure;
– increase the production and supply of digital content;
– ensure the digital transformation of the administration and
businesses;
– promote digital culture by generalizing
the use of ICTs in society;
– strengthen digital trust;
– develop a local digital industry and encourage research and innovation;
– ensure the development of human capital and
digital leadership;
– ensure the improvement of governance and institutional support.
All sectors of activity now have a
reference framework, which will facilitate the readability and visibility of the
actions that the Government intends to carry out in the field of
the digital economy, in order to make it one of the levers priorities
of industrialization in Cameroon and of economic development.
Philémon Yang
Prime Minister, Head of Government
INTRODUCTION
In his address to the nation on December 31, 2015, the Head
of State recalled the driving role of the digital economy
in economic growth and job creation. The
telecommunications and ICT sector is at the heart of this
digital economy, given its potential contribution
to human and economic development.
Indeed, the digital economy has three dimensions. The first, which is described as the heart of the digital economy, is based in particular on the development of
broadband electronic communications infrastructures, but also
on the development of the IT and
electronics sectors.
The second dimension relates to the activities born out of the
development of the digital economy. These activities are
referred to as the new economy, and only exist thanks to
the digital core, ie the broadband infrastructure
and the Internet.
The third dimension concerns the transformation of
existing sectors of activity, by integrating the use of ICTs, in
the performance of activities in these sectors: administration,
posts, tourism, trade, etc.
The digital economy is today a vector of growth, productivity and competitiveness of companies and
countries. Its transversal character impacts all sectors of
the economy, it is also at the origin of new innovative sectors and has made others dependent on it.
As such, Minpostel’s sectoral strategy has defined as a
strategic objective “to increase quantitative, qualitative and
low-cost access to electronic communications services
throughout the national territory”. The challenge for Cameroon in the field of communications
and telecommunications infrastructure is to capitalize on the achievements, to
develop the broadband infrastructure in order to allow the integration of our country into the global knowledge economy.
Faced with this challenge, the “Digital Cameroon 2020” plan
focuses on the definition of strategic axes, actions and
priorities with a strong impact on the digital development of the territory, the intensification of the use of ICT services;
the fight against poverty by creating jobs and increasing
the growth rate of the national economy.
The implementation of this plan requires cross-cutting actions such as improving governance, strengthening human capital and digital confidence, taking environmental aspects into account and making adequate financial resources available.
STATE OF PLAY AND DIAGNOSIS OF THE DIGITAL ECONOMY IN CAMEROON
EVOLUTION OF SOME KEY INDICATORS AT THE NATIONAL LEVEL
STATE OF PLAY AND DIAGNOSIS
1. State of play
The opening to competition of the telecommunications sector in Cameroon is enshrined in Law No. 98/014 of July 14, 1998 governing
telecommunications in Cameroon. With this law, the State will disengage from the productive sector of telecommunications through the separation
of the activities of exploitation, supervision, regulation and regulation
. Given the technological evolution, the regulatory framework will undergo changes with the promulgation of a set of
laws, repealing the aforementioned law.
Thus, under the terms of Laws No. 2010/013 governing electronic communications in Cameroon and No. 2010/12 relating to cybersecurity and
cybercrime in Cameroon, the Administration in charge of Telecommunications on the one hand, ensures the implementation implementation of the Telecommunications and Information and Communication Technologies sectoral policy and, on the other hand, develops and implements the
security policy for electronic communications and information systems.
ART ensures, on behalf of the State, the regulation, control and monitoring
of the activities of operators and operators in the Telecommunications and Information and Communication Technologies sector;
it also ensures compliance with the principle of equal treatment of
users in all electronic communications companies and collaborates with ANTIC for the regulation of electronic
security activities .
ANTIC’s mission is to promote and
monitor government action in the field of
information and communication technologies; it is responsible for regulating
electronic security activities, in collaboration with the
Telecommunications Regulatory Agency (ART).
The operation of the networks with a view to providing telecommunications services
is carried out by operators holding
public service concessions, Internet access providers and
value-added service providers in particular. The telecommunications services market includes 3 mobile operators, MTN Cameroon, Orange Cameroon and Viettel Cameroon; a fixed telecommunications operator
, Camtel, which also plays the role
of transport operator.
1.1. Evolution of some key indicators at the national level
a) Sectors producing ICT services in Cameroon
This sector is at the heart of the digital economy. The question of the development of electronic communications infrastructures is at the
heart of the emergence of the digital economy. The aim here is to take
stock of these so-called structural indicators of the digital economy. These
indicators are:
– The telecommunications and ICT services market
– telecommunications
equipment manufacturers – IT equipment
– consumer electronics
– components/systems
– game software publishers
– IT services
EVOLUTION OF SOME KEY INDICATORS AT THE NATIONAL LEVEL
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020
STATE OF PLAY AND DIAGNOSIS
Telecommunications and ICT services market indicators
Number of subscribers to fixed telephony including CDMA
Number of subscribers to mobile telephony The mobile telephony penetration rate was around 80% in
2015*. However, if we take into account the fact that this indicator
refers more to the number of chips sold, and by estimating that 30%
of the park has more than one chip, the real penetration rate would be
around 50%.
Number of Internet subscribers
* 2015 data is an estimate.
11
EVOLUTION OF SOME KEY INDICATORS AT THE NATIONAL LEVEL
2020 Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan
STATUS
AND DIAGNOSIS
Fixed telephony and CDMA market
revenue Mobile telephony
revenue – Mobile market turnover in billions of FCFA
– Monthly tariffs excluding taxes for CAMTEL Internet specialized links
– April 2015
• Telecommunications equipment
manufacturers Cameroon remains an importer of telecommunications equipment telecommunications.
The sectoral strategy provides for the development of a telecommunications industry
. The technology park creation project, whose
additional studies will be financed by the AfDB, is part of this logic.
• Computer equipment
Cameroon is an importer of computer equipment.
• Consumer electronics
This sector of activity is not yet developed in Cameroon.
12
EVOLUTION OF SOME KEY INDICATORS AT THE NATIONAL LEVEL
2020 Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan
STATUS
AND DIAGNOSIS
• System components
Cameroon remains an importer in this sector.
• Software
publishers A local market for software publishers exists.
• Computer services
Several local companies or subsidiaries of foreign companies provide
computer services in Cameroon. But there are no data
to assess this sector.
b) The new economy sector
This concerns digital content, the emergence of which is linked solely to
the emergence of digital (See digital market indicators
).
• Online commerce
There are a few Cameroonian sites offering
online commerce. But to better assess the state of play in this sector, the following indicators must be provided:
– number of e-merchants;
– revenue from e-commerce;
– number of online transactions.
• Broadband Internet Broadband Internet
usage is a prerequisite for the development of the digital economy. According to the ITU, the broadband Internet access rate
was 4% in Cameroon in 2015.
• Online media and content
The market for digital products such as online media, online cultural products, the video game market, the communication market… is nascent and already very dynamic in Cameroon. Provisions
at the institutional and regulatory levels should make it possible
to better supervise this sector.
c) The digital transformation sector
• Administration: e-gov
A survey carried out in 2013 revealed the level of ICT equipment in the Administrations, as illustrated in the graphs below:
Number of computers per 100 people in the central services of
Public Administrations
The average penetration rate in the central services of ministries and
of certain administrations and institutions is around 42%, or 42 computers per 100 people. The Ministry for the Promotion of Women
and the Family is the least endowed, with a 5.9%
computer penetration rate. With respectively 133% and 125% of equipment rate,
MINEPDED and MINADER are the best equipped in terms of computers. MINPOSTEL
remains well below the average, with a
penetration rate of only 23.8%.
The average Internet speed per Administration is 4 Mb/s, or approximately
1.55 Kb/s per head, which is well below the objective of
broadband access, which should turn on average around 2Mb/s per head.
EVOLUTION OF SOME KEY INDICATORS AT THE NATIONAL LEVEL
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020
STATE OF PLAY AND DIAGNOSIS
• Bank: eBanking
Level of adoption of ICT by local financial institutions: access
to ICT for all banks is a reality.
Ongoing activities such as mobile banking and mobile money will improve the rate of banking in Cameroon, which is
around 12% today.
• Health: e-health initiative
04 hospitals in Cameroon are connected to a
telemedicine network.
The development of applications such as the cardiopad, GiftedMoon
will improve people’s access to health services.
• Education: e-education
– 28 out of 33 state university sites are connected to the Internet;
– 50 high schools are connected to the Internet;
– number of digital libraries. There is no digital library worthy of the name yet.
• Culture and tourism
The platform for the digitization of tourist and cultural heritage
currently being deployed.
d) Cybersecurity
• Indicator of the electronic certification market
There is a certification authority, ANTIC, and the number of
secure applications is 05 to date.
Banks, subsidiaries of multinational companies secure their data
using PKIs made available by their parent company (Ecobank, SCB,
SGBC, Standard, etc.).
The BEAC also has its own PKI.
ANTIC is in talks with APECCAM to secure the applications used by banking establishments within APECCAM.
ANTIC’s PKI needs to be upgraded for
international mutual recognition. A project is underway with the AfDB in
this direction.
• CIRT
There is currently a CIRT set up by ANTIC. A project to
strengthen this CIRT is underway.
14
POSITIONING OF CAMEROON AT THE INTERNATIONAL
LEVEL IN THE FIELD OF DIGITAL
Cameroon Digital Strategic Plan 2020
STATE OF PLAY
AND DIAGNOSIS
Source: WEF, Global Information Technology Report 2015
Several organizations at the international level have retained various indices and
rankings to present the level of development of the ‘economy
or some of its essential components in the countries,
sub-regions, regions as well as at the global level.
The best known of these indices are:
– The Network Readiness Index (NRI) produced by the World Economic Forum
– The E-Government Development Index (EGDI) which is produced
annually by the Department of Business Economic and Social Affairs of the United Nations General Secretariat;
– The Cybersecurity Index (GCI) from the ITU.
These different indices reflect the absolute situation of the world economies in the different axes that make up the digital economy.
The situation in Cameroon is as follows:
a) “NRI” index *
With a value of 3 on a scale of 1 to 7, Cameroon ranks
126th in the world out of the 143 countries assessed. It is considered a
middle-low country. The low ranking of Cameroon is due in particular to the
low development of infrastructures whose value is 1.2, to the low
individual use with a value of 1.9 and to the unaffordable costs.
(*) Network and Readness Index, measures the ability (factors, policies, institutions) of States to be ready to use and take
advantage of the opportunities offered by ICTs to increase the competitiveness of the economy and the well-being of populations.
1.2. Positioning of Cameroon at the international level in the digital field
POSITIONING OF CAMEROON AT THE INTERNATIONAL
LEVEL IN THE FIELD OF DIGITAL
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020
STATE OF PLAY AND DIAGNOSIS
b) “E-Gov” Development Index
This index for which Cameroon displays a value of 0.2782
on a scale of 0 to 1, integrates three pillars, namely infrastructure, human capital and online services.
On these pillars, Cameroon displays respectively the values of
0.0958; 0.5421; and 0.1968 on a scale of 0 to 1.
If the situation of human capital is acceptable, that of infrastructures and online services is less enviable.
Cameroon thus ranks second in the Central African sub-region
, behind Gabon, whose index value is 0.3294. In
Africa, Tunisia ranks first with 0.5390 and
globally, the Republic of Korea is ranked first with 0.9462.
(*) EGDI measures the use of ICT by the government to provide information and public services to users. The EGDI index is the average of three indices:
online services (Online Service Index: OSI), telecommunications infrastructure (Telecommunications Infrastructure Index: TII), human capital (Human Capacity Index: HCI)
16
POSITIONING OF CAMEROON IN PLAN INTERNATIONAL
IN THE DIGITAL FIELD
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020
STATE OF PLAY AND DIAGNOSIS
Source: United Nations Department Public Administration Country studies – 2014
POSITIONING OF CAMEROON AT THE INTERNATIONAL
LEVEL IN THE FIELD OF DIGITAL
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020
STATE OF PLAY AND DIAGNOSIS
c) “GCI” Cybersecurity Index *
Compared to this indicator, Cameroon is ranked 5th in Africa and 15th ex quo
in the world. This indicator shows that the current level of access to ICT enjoys an
acceptable level of security.
The level of these indicators sufficiently shows that Cameroon has efforts to make, particularly in the development of telecommunications
infrastructure .
The development of these infrastructures is the
prerequisite for the improvement of the other components of these
indicators.
Source: April 2015 Report, Global Cybersecurity Index and Cyber Wellbeing Profiles Source: ITU (GCI Interactive Comparison Tool)
(*) GCI measures each country’s level of development in cybersecurity. It presents the country’s commitment/readiness to cybersecurity.
DIAGNOSTIC ANALYSIS
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020
STATE OF PLAY AND DIAGNOSIS
2. Diagnostic analysis
The diagnostic analysis of the state of play and the diagnostic analysis made
in the revised telecommunications sector development strategy document
in 2015 made it possible to identify the main problems below, which hinder the development of
the economy digital in Cameroon. These problems are classified
into three categories, namely, those that hinder the supply of services,
those that prevent boosting demand and finally those relating to
good governance, regulation and training.
On the supply side – Absence of a broadband
infrastructure development master plan ; – The poor development of broadband infrastructure;
– Quantitative and qualitative lack of infrastructure;
– Low coverage of 3G and 4G mobile networks;
– The monopolistic structure of the national and international bandwidth access market and the non-regulation of these market segments, implying high retail tariffs;
– The weak transformation of business sectors, due to the low
availability of ICT solutions;
– Absence of a local
digital content development industry;
– Research and innovation not sufficiently supervised.
On the demand side
– Weak digital transformation of society
– Very low rate of access to broadband Internet by households
– Low rate of access to very high-speed internet by companies
– A weak culture in the use of ICTs
– Still high retail prices
– Low dematerialization of public services
– Low availability of online services
On the side governance and training
– The trust framework in the digital economy not sufficiently adapted.
– Failure to adapt the current regulatory framework to the development of the digital economy and the not yet
completed publication of the implementing texts of the three laws to make the
legal and regulatory framework more suitable;
– Failure to adapt the institutional framework to the development of
the digital economy
– Weakness of regulation for support for the
development of the digital economy;
– Inadequacy of training in relation to employment needs in
the field;
– Insufficient financial resources.
CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES OF THE DIGITAL ECONOMY
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020
CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES
In terms of human and economic development
The major challenge of Cameroon’s evolution towards the digital economy is to create added value in order to improve the
standard of living and social well-being of Cameroonians.
The effective use of information and
communication technologies in all areas of economic
and social life is a priority to ensure sustainable economic growth in Cameroon.
Telecommunications constitute one of the most important sectors of the economy of Cameroon, with a contribution to the
GDP of nearly 5%, representing a turnover of more than
more than 538 billion FCFA during the year 2014 by
operators holding a public service concession only*.
The cumulative volume of investments by concession operators
is estimated at nearly 1,387.17 billion FCFA between June 1998
and December 2013. Since 2010, investments by concession operators amount to more than 100 billion FCFA per
year, i.e. nearly 6% of total annual investments in Cameroon. To this figure should be added the investments made by other service providers and other services
in the sector, not subject to the concession system.
With regard to improving business productivity
– the ability of companies to collect, produce and manage information has become the essential vector of
economic growth, productivity, competitiveness and innovation;
Source: MINPOSTEL
Source: MINPOSTEL
(*) Camtel, Orange, MTN, Nexttel.
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020
CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES
– the rate of penetration of ICT in companies, in particular SMEs, and their widespread and effective use play
a key role in the development of a
knowledge economy and in the ability of companies to produce
greater added value and to create new sources
of employment. However, in Cameroon, the economic fabric is essentially made up of SMEs, which have little access to this information society.
It is therefore necessary:
– to meet industry requirements in terms of quality, cost and delivery times for
ICT services;
– to develop new processes for the creation of
professions in the digital ecosystem, in particular through
appropriate training modules throughout the
vertical, horizontal and online training chain.
In terms of access to knowledge: main challenge for
the citizen
– ICTs and the Internet facilitate communication and access to
knowledge and knowledge. They allow citizens, beyond easy and rapid access to information,
considerable time savings, in particular thanks to the availability
of remote services.
– In this context, after the advances made in terms
of equipping citizens with mobile telephony, the next step would be to accelerate the process of democratization of the Internet at home and encourage rapid adoption of new technologies by citizens in their
everyday life.
For research, development and innovation
The challenge is to create greater proximity between researchers
from the academic world and companies, to allow better focus on concrete and innovative projects supported
by industrialists and a more appropriate balance between fundamental research and applied research geared towards
market opportunities.
Regarding the creation of a local ICT industry.
Whether in terms of content or infrastructure, the creation
of a local ICT industry remains an important issue for
Cameroon. Its implementation constitutes a major source
of growth and jobs.
The challenges for administrations: improving efficiency
and reducing costs.
The implementation of electronic governance (e-government) through simplified and automated processing of information will enable the public sector to achieve significant gains
in effectiveness and efficiency.
DIGITAL CAMEROON 2020 STRATEGIC PLAN:
STRATEGIC CHOICES
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020
DIGITAL CAMEROON STRATEGIC PLAN
VISION:
“Make Cameroon a digital country by 2020”
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 24 DIGITAL CAMEROON
STRATEGIC PLAN The strategic plan for the development of the digital economy is anchored in the Cameroon 2035 vision, the DSCE, the development strategy for the telecommunications and ICT validated in 2005 and revised in 2015. This last strategy has the vision of “making Cameroon a digital country”. This strategic plan is based on eight axes built around the three main dimensions of the digital economy: infrastructure, the new economy and the transformation of other sectors of activity by ICTs and aspects relating to
supply, demand and governance.
The development of the service offer in the
digital economy is dealt with around the following axes:
– Developing broadband infrastructures;
– Increase the production and supply of digital content
;
– Develop a local digital industry and encourage research and innovation;
With regard to actions to boost demand,
they are carried out in the following areas:
– Ensuring the digital transformation of the administration
and companies;
– Promote digital culture by generalizing
the use of ICTs in society;
Aspects relating to governance and regulation in
the development of the digital economy are
broken down into the following areas:
– strengthening digital trust;
– ensure the development of human capital and digital leadership;
– ensure the improvement of governance and institutional support.
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 25 DIGITAL CAMEROON
STRATEGIC PLAN STRATEGIC AXES 1. Develop broadband infrastructure; 2. Increase the production and supply of digital content; 3 Ensure the digital transformation of the administration and businesses; 4. Promote digital culture by generalizing the use of ICTs in society;
5. Building digital trust;
6. Develop a local digital industry and encourage research and innovation;
7. Ensure the development of human capital and leadership in digital;
8. Ensure improved governance and institutional support.
Indicators
ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT
Contribution of digital to GDP*
Number of direct jobs created in digital
Average annual contribution of the sector
in terms of taxes and duties
SOCIAL DEVELOPMENT
% of households with Internet
access % of Internet access broadband
in large enterprises
% population with broadband access
fixed to home (at least 2 Mbits)
% population with mobile broadband access
Rural population served by
community access point
Average cost of Mbit/s per month (Fcfa)
INTERNATIONAL POSITIONING
e-Government Development Index (EGDI)
Networked Readiness Index “NRI”
Cybersecurity Index “GCI”
26
NUMBERED OBJECTIVES ON THE HORIZON 2020
Digital Cameroon 2020 strategic plan
Strategic Axis 1: DEVELOP BROADBAND INFRASTRUCTURE
Digital Cameroon 2020 Strategic Plan DIGITAL CAMEROON
STRATEGIC PLAN
Strategic objective 1: Generalize broadband access for citizens, businesses and households.
Specific objectives:
– increase fixed teledensity to 45% by 2020;
– increase mobile teledensity to 95% by 2020;
– raise the broadband penetration rate to 20% by
2020;
– increase the Internet penetration rate for households to 20% by
2020;
– reduce the cost of access to broadband services to less than 5% of the
average monthly income of a citizen by 2020;
– raise the Internet penetration rate from 11% in 2016 to 50%
in 2020;
– increase the international bandwidth per Internet user
to 2 Mbits/s.
Actions/initiatives
– Connect all departmental capitals to the national fiber optic backbone by 2018;
– Connect all the district capitals to the national fiber optic backbone by 2020;
– Build the landing points of the ACE and CBSC submarine
cables, activate them and make them operational;
– Provide Cameroon with a satellite infrastructure;
– Encourage private investment in transport and access infrastructure;
– Promote low-cost access technologies;
– Develop wired access networks using FTTX technology;
– Optimize the use of landing points for submarine cables;
– Ensuring the high-speed connection of the administrations;
– Ensure the broadband connection of all high schools;
– Continue the broadband connection of all post offices;
– Ensure the broadband connection of all postal contact points
;
– Ensure high-speed connection of all TCPs;
– Ensure free access to national content in public spaces;
SYNTHESIS
Implement a real policy of digital development
in Cameroon through the quality of its infrastructures, guaranteeing broadband access throughout the territory and very high
speed for certain priority areas, in order to develop the digital intensity of companies and citizens, and to improve
connectivity with the countries of the Central African sub-region.
Strategic Axis 1: DEVELOP BROADBAND INFRASTRUCTURE
Digital Cameroon 2020 Strategic Plan
DIGITAL CAMEROON STRATEGIC PLAN
– Encourage infrastructure sharing;
– Ensure coordinated implementation of transport infrastructure;
– Ensure the migration of networks from Internet Protocol Version 4 to
Version 6 (IPv4/IPv6);
– Ensure the orientation of tariffs towards costs;
– Make TCPs real exchange spaces; – Include the laying of transport network pipelines in
the road and rail infrastructure markets . – Include in the contracts for access roads to new or old neighborhoods and for the construction of social housing, the laying of pipes for the access and internal distribution network in the housing.
– Develop, in collaboration with the decentralized local authorities, the master plans for digital development;
– Extend the construction of 3G/4G mobile access networks;
– Build Datacenters for the administration and companies
and promote Cloud technologies and the rational management
of metadata (Big data);
– Ensure compliance with norms and standards in the establishment
of infrastructure;
– Install WiFi everywhere in public spaces in large cities.
Strategic Axis 2: INCREASE THE PRODUCTION AND OFFER
OF DIGITAL CONTENT
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020
DIGITAL CAMEROON STRATEGIC PLAN
Strategic objective: To have attractive content developed and
hosted at local level
Specific objectives:
– to develop national digital content and increase the visibility of Cameroon through the .cm
– to host at local level 70% of national content;
– make Cameroon’s image more visible on the Internet;
– create an environment conducive to the development of
local content.
Actions/initiatives
– Make the government web portal functional;
– Digitize and disseminate the national tourist and cultural heritage;
– Promote the development of e-application content in
all sectors of activity including health, tourism, education, transport, agriculture;
– Give awards each year to the best applications in
favorable sectors of activity (health, education, agriculture);
– Establish and make freely available the digital map of Cameroon, in order to promote the development of applications and services using Geographic Information Systems;
– Digitize and put the national archives online;
– Promote the establishment of local e-commerce platforms
(books, music, films, etc.);
– Promote the development of fun activities (games, leisure)
online;
– Promote the national .cm domain;
– Produce content in national languages, particularly in
the education sector;
– Promote local content fairs/fora;
– Promote the gender perspective in the development of content;
– Encourage the creation of online educational content;
– Set up an offer of multi-channel IP interconnection services
(Voice, SMS, USSD) by concessionary operators for
alternative VAS mobile access operators.
SUMMARY
Develop and structure the ICT sector and ecosystem to capture
opportunities and increase the added value of the
digital economy for the benefit of Cameroon.
30
Strategic Axis 3: ENSURING DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION
ADMINISTRATION AND COMPANIES
Digital Cameroon 2020 Strategic Plan DIGITAL CAMEROON
STRATEGIC PLAN Strategic objective: Accelerate the digital transformation of the administration and companies to increase their efficiency, transparency, competitiveness and productivity. Specific objectives: – raise the E-Gov Development Index from 0.2782 to 0.50 by 2020; – make 100% of administrative forms available online; – raise the NRI index to 4.5 by 2020; – raise the Online Services Index defined by the United Nations from 0.1524 to 0.4 by 2020; – carry the E-participation index defined by the United Nations of 0.1571
to 0.3000 by 2020.
Actions/initiatives
– Set up a government intranet;
– Set up a portal giving access to all public services;
– Set up a robust messaging system for the administration (@x.gov.cm);
– Dematerialize administrative procedures;
– Develop and Promote Digital in the administration;
– Implement, by 2018, the following flagship services and projects:
• online response files for Public Contracts;
• social declarations for employees with the CNPS;
• online declaration and payment of taxes;
• Customs declaration;
• dematerialization of import and export procedures. ;
• civil status and local authority information system;
• e-schooling platform / online registration;
• electronic visa.
– Implement, by 2020, all
e-government services and projects;
– Facilitate online payments;
– Develop universal Marketplaces;
– Develop and promote eTourism;
– Develop and promote eRetail and eLogistic;
– Develop and promote eHealth;
– Develop and promote online postal services;
SUMMARY
This axis relates to actions to be taken so that the digital revolution transforms the traditional sectors of activity, and allows
companies and structures in these sectors to also offer their
services virtually (thanks to the broadband telecommunications infrastructure and the Internet), in order to increase their number
of users, as well as the added value linked to their activities.
31
Strategic Axis 3: ENSURING THE DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION
OF THE ADMINISTRATION AND BUSINESS
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 DIGITAL CAMEROON
STRATEGIC PLAN – Raise awareness among businesses of the importance and impact of the digital transition; – Develop for each sector, a self-diagnosis tool adapted to
its specificities in order to help companies assess their level of maturity in digital transition and identify the opportunities offering
the most benefits along their value chain;
– Supporting the digital transition through an offer of
certified coaching structures;
– Approve technology coaching training centers;
– Encourage business groups to activate digital (dissemination of good digital practices within the sector, pooling of cross-cutting ICT needs, Open source vision, Cloud, etc.);
– Encourage exchanges and the promotion of “success stories” of digital transformation by and for Cameroonian companies,
through meetings;
– Set up a shared resource center with
studies and recommendations on the digital transition and facilitate
their dissemination;
– Conduct ICT impact studies in all production sectors;
– Set up a telepresence platform in the
Cameroonian administration;
– Promote the establishment of local e-commerce platforms
(books, music, films, etc.);
– Make digital transactions between the administration
and businesses mandatory;
– Continue training in ICT tools in all administrations;
– Ensure the availability and implementation of an ICT master plan by all administrations.
32
Strategic Axis 4: PROMOTE DIGITAL CULTURE THROUGH
THE GENERALIZATION OF THE USE OF ICT IN SOCIETY
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 DIGITAL CAMEROON
STRATEGIC PLAN Strategic objective: Improve the quality of life of the citizen through better use of digital Specific objectives: – bring to 5% the Internet penetration rate for households at 2 megabits by 2020; – raise the broadband Internet penetration rate of companies with at least five employees to 50% by 2020; – increase the number of commercial sites to 20%; – increase the rate of households with Internet access from 6% to 20%;
– raise the high-speed Internet access rate to 95% in large
companies;
– increase from 4% to 10% the rate of the population having
fixed broadband access at home (at least 2 Mbits);
– raise to 65% the rate of the population with mobile broadband access
; – reduce the rural population served by a community access point
from 47,000 to 10,000 ; – go from 23,000 to 10,000, the average cost of digital services per user per year (Fcfa). . Actions/initiatives: – Establish incentive mechanisms and promote access to and use of digital technology among citizens; – Facilitate the acquisition of terminal equipment and access for
certain sections of the population (teachers, students, researchers, community centres, etc.);
– Develop public e-services for mandatory use by the citizen;
– Develop skills and uses of digital technology within the
Administrations;
– Encourage legal persons to use transactional services;
– Ensure free access to national content in public spaces;
– Promoting lower service costs;
– Promote e-commerce;
– Offer the user secure access to online services;
– Set up national messaging in “.cm”.
SUMMARY
The digital revolution will only have its full meaning if society
as a whole adopts ICT in its way of life. Thus,
the advent of the digital economy in Cameroon will inevitably pass
through the generalization of the use of ICT by individuals, administrations and businesses.
33
Strategic Axis 5: STRENGTHENING DIGITAL CONFIDENCE
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 DIGITAL CAMEROON
STRATEGIC PLAN Strategic objective: Put in place favorable conditions to create confidence in the digital economy Specific objectives: – raise the GCI cybersecurity index from 0, 41 at 0.65; – secure 100% of government applications; – secure all public administration websites;
– increase the number of secondary certification authorities from 0 to 10;
– increase the number of approved security auditors from 7 to 50;
– sign two mutual recognition agreements in the field
of electronic certification;
– organize ten awareness campaigns (weekly radio/TV broadcasts, daily advertising spots, leaflets, regular postings
, SMS messaging and social networks (Facebook, Twitter, etc.);
– strengthen the operationalization of the national CIRT and increase the number of
CIRT by sector of activity from 0 to 5 (banking, industry, education,
health, defence);
– secure all national critical information infrastructures;
Actions/initiatives
– Securing electronic transactions;
– Identify and secure national critical infrastructures;
– Raising the awareness of the administration, companies and citizens to
electronic security;
– Encourage research/development and innovation in the field of electronic security;
– Set up a PKI developed by national expertise with a view
to mastering this technology, and promoting trade
and electronic transactions;
– Finalize and monitor the implementation of the national
network and information systems security policy;
– Develop procedures and standards for securing
electronic communications networks;
– Make an inventory and diagnosis of applications and databases of public administrations and institutions;
– Disseminate guides to good practices in electronic security;
– Strengthen and coordinate awareness-raising initiatives;
– Strengthen international cooperation in the field of cybersecurity, and
the fight against cybercrime and cyberterrorism;
SUMMARY
This concerns all the actions to be taken to guarantee
citizens’ confidence in the digital economy. These actions aim in particular to secure the Cameroonian cyberspace.
34
Strategic Axis 5: STRENGTHENING DIGITAL CONFIDENCE
Digital Cameroon 2020 Strategic Plan
DIGITAL CAMEROON STRATEGIC PLAN
– Encourage Public-Private Partnership for securing critical infrastructure;
– Ensure the adequate protection of the personal data of citizens
;
– Increase awareness of personal data protection issues from an early age;
– Encourage organizations to have internal cybersecurity managers;
– Set up redundancy of the national PKI;
– Train magistrates, police officers and legal assistants on cybersecurity, the fight against cybercrime and cyberterrorism, and on
the appropriation of texts in the sector;
– Promote the integration of experts in cybersecurity, the fight against
against cybercrime and cyberterrorism, in
traditional security professions;
– Strengthen the surveillance of national cyberspace in order to minimize the
number of cybernetic incidents;
– Develop a secure architecture for the development of websites
and make available the use of SSL certificates;
– Set up incoming and outgoing traffic control
points at landing points (submarine, etc.)
35
Strategic Axis 6: DEVELOP A LOCAL DIGITAL INDUSTRY
AND ENCOURAGE RESEARCH AND INNOVATION
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 DIGITAL CAMEROON
STRATEGIC PLAN
Strategic objective: Develop locally produced digital goods and services at the national level
Specific objectives:
– bring to 50% the rate of computers and other ICT equipment marketed in Cameroon from local industry;
– reduce imports of ICT goods and services by 50%;
– multiply by 50 the number of ICT research and development programs conducted by universities in partnership with companies;
– support the creation of at least 20 start-ups per year in the digital field;
– create a technology park for the digital economy;
– create 08 digital study and research institutes within
universities;
– create two innovation centers in the digital field.
Actions/initiatives
– Prioritize locally produced ICT goods and services in public orders;
– Create digital study and research institutes in
all state universities;
– Strengthen the broadband connection of universities and create digital laboratories;
– Create a framework/platform for exchanges between the government and business
groups for the development of the digital economy;
– Facilitate the establishment of foreign companies/investors in national technology parks;
– Labeling and awarding prizes each year to the best ICT products in various
sectors of activity;
– Organize annual ICT fairs and fora;
– Establish an environment conducive to the development of the digital economy;
– Promote the culture of Digital Innovation;
– Stimulate innovation within public administration, universities and colleges, research centers and businesses;
– Encourage the establishment of
electronic security research/development centers (rise to 5 in 2020);
– Invent financing mechanisms for public and private innovation;
SUMMARY
Through this axis, it is a question of adapting the governance of the industrial sector to the challenges of digital technology, of encouraging the development
of the creation of local digital companies, of developing
centers of excellence in digital innovation
.
36
Strategic Axis 6: DEVELOP A LOCAL DIGITAL INDUSTRY
AND ENCOURAGE RESEARCH AND INNOVATION
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 DIGITAL CAMEROON
STRATEGIC PLAN – Encourage and facilitate the access of SMEs and start-ups to public contracts, in particular through the total or partial reservation of some ; – Use public procurement as a lever to support the innovation capacity of companies and for the development of new technological building blocks; – Consider fiscal or regulatory measures to support start-ups in certain promising sectors;
– Establishment of a venture capital fund to finance start-ups;
– Implementation of a technology transfer strategy between companies and research and innovation structures;
– Establishment of industrial free zones for the production of digital equipment;
– Support for the establishment of assembly/manufacturing industries for
digital terminals and equipment;
– Support for the establishment of a local industry for the development of
“made in Cameroon” applications;
– Setting up digital incubators;
– Establishment of clusters;
– Establishment of a waste treatment center for
electrical and electronic equipment;
– Establishment of a national network of R&D institutes in the
digital field;
– Creation of intellectual property and
technology transfer management offices within innovation structures;
– develop business/start-up interfaces to stimulate digital ecosystems;
– Set up a platform for referencing digital SMEs
for public buyers;
– Encourage the creation of digital manufacturing workshops (fab labs).
37
Strategic Axis 7: ENSURE THE DEVELOPMENT OF HUMAN CAPITAL
AND LEADERSHIP IN DIGITAL
Cameroon Digital Strategic Plan 2020 DIGITAL CAMEROON
STRATEGIC PLAN
Strategic objective: ensure the availability in quality and quantity
of human skills able to meet the needs of
the digital economy.
Specific objectives:
– ensure the digital connectivity of national education and training institutions (e-accessibility);
– develop online educational services (e-learning);
– develop centers of excellence;
– provide training and capacity building for the needs
of the digital economy.
Actions/initiatives
– Train 2000 ICT engineers in the period 2016-2020;
– Increase the percentage of universities/grandes écoles having set
up a PPP in the digital economy to 10%;
– Increase to 50% the rate of secondary education establishments
having multimedia laboratories with high-
speed internet connection;
– Increase to 100% the rate of engineering students equipped with laptops and
individual high-speed internet connection;
– Connect 30% of basic education establishments to
high-speed Internet by setting up multimedia centres;
– Ensure free training in digital sectors;
– Exempt from taxes on the acquisition of ICT equipment by pupils,
students and schools and universities;
– Recruit specialists in network and information systems security and in digital investigations (1,000 by 2020);
– Encourage certification training and capacity building for public administration staff in ICT
and electronic security;
– Encourage the inclusion of digital security in teaching programs at all school and university levels (rise to 50% of training establishments by 2020);
– Strengthen capacities in digital security;
– Adapt training to the niches of professions in shortage and
of the future identified by the players in the sector;
SUMMARY
Digital illiteracy is a major obstacle to the advent
of the information society. To this end, building the capacity of human resources becomes a priority, to make
Cameroon a digital country by 2020.
38
Strategic Axis 7: ENSURE THE DEVELOPMENT OF HUMAN CAPITAL
AND LEADERSHIP IN DIGITAL
Cameroon Digital Strategic Plan 2020 DIGITAL CAMEROON
STRATEGIC PLAN – Create a network of centers of excellence in digital engineering; – Implement training programs for the digital transition of professions; – Build and Equip Regional Learning and Training Centers in ICTs; – Generalize the creation of IT courses in schools; – Support the development of women’s skills in the field of digital engineering;
– Provide students with
qualifying training leading to certification as part of their course;
– Create e-Employment Pilot Centers in the regional capitals;
– Expand the Youth Entrepreneurship Information Centers
(CIIEJ);
– Include the computer network in the CAD for the construction of training centres;
– Accelerate the development and use of digital simulation
– Support technological and scientific vocations among
women;
– Increase the professionalization of teaching by establishing
agreements between universities and schools and certification publishers (CISCO, Microsoft, Oracle, etc.);
– Strengthen the training of engineers and equivalents as well as the professional training of senior technicians in the field of ICT
– Develop training in the digital humanities;
– Rely on the Cameroonian diaspora to support
young entrepreneurs in the digital sector, through training
and online mentoring.
39
Strategic Axis 8: ENSURE THE IMPROVEMENT OF GOVERNANCE
AND INSTITUTIONAL SUPPORT
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 DIGITAL CAMEROON
STRATEGIC PLAN Strategic objective: Create an environment conducive to the development of digital technology for economic development. Specific objectives :
– improve the legislative and regulatory framework to adapt it to the development of the digital economy;
– reorganize the institutional framework to better adapt it to the development of the digital economy;
– provide financial support for digital development
.
Actions/initiatives
– Adapt the legislative framework to put local authorities at
the heart of infrastructure development in their territory;
– Regulate the mandatory fiber optic pre-cabling of new buildings;
– Take into account in the contracts for the development of urban roads and the construction of social housing, the pipes
of the fiber optic access network and internal distribution in
the housing;
– Adapt legislation on cyber-security and cybercrime,
cyber-terrorism, electronic commerce, intellectual property, in order to take into account the requirements of the digital economy;
– Develop a tax and customs regime that encourages the development of
the digital economy;
– Develop a text on the protection of personal data;
– Develop a national legal framework for venture capital financing;
– Take incentive, regulatory and tax measures for any
investment in digital research and innovation;
– Draw up a law on online access to administrative documents
of public institutions;
– Adapt the law on public-private partnership to the field of the digital economy;
– Adapt the law on the electronic transfer of funds;
– Develop a law governing online payments;
– Create a national infrastructure and transport company in
the field of electronic communications;
SUMMARY
The implementation of cross-cutting activities such as the audit of the
legal and regulatory framework with a view to adapting it to the
digital economy, the mobilization of the financing necessary for the
implementation of all the projects identified, are all factors essential to the emergence of the information society
in Cameroon.
40
Strategic Axis 8: ENSURE THE IMPROVEMENT OF GOVERNANCE
AND INSTITUTIONAL SUPPORT
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 DIGITAL CAMEROON
STRATEGIC PLAN – Establish a coordination body for public infrastructure works integrating the various administrations ( public works, transport, telecommunications, broadcasting, energy, water, urban development, etc.); – Set up a national observatory and regional observatories of e-commerce services; – Create a consultation framework for multi-sector regulators to coordinate the sharing of infrastructure and encourage the sharing of infrastructure between the different sectors;
– Set up a framework for consultation between the principal, the principal
and the organizations financing the digital economy;
– Set up a common identification platform for e-commerce network subscribers;
– Set up security monitoring centres/laboratories;
– Set up a strategic watch structure for the development of the digital industry; – Set up a national ISRC (International Standard Recording Code)
code agency ; – Develop the national cyber-security strategy and the master plan for securing e-commerce networks; – Subsidize teachers’ equipment with computers and Internet connections;
– Subsidize the equipping of pupils and students with
laptops and internet connections;
– Set up a competitive public-private fund for
digital R&D;
– Set up a venture capital fund to finance start-
ups;
– Reduce the cost of high-speed Internet access in higher education establishments;
– Encourage companies to use local software;
– Supervise the security of electronic exchange platforms
by ensuring compliance with the standards and levels of security in force
;
– Reread the laws on electronic communications, commerce
electronics, intellectual property, cybersecurity, cybercrime and cyber-terrorism in Cameroon, involving all
stakeholders;
– Facilitate the establishment of foreign companies/investors in
national technology parks;
– Invent financing mechanisms for public and
private innovation;
– Consider tax or regulatory measures to support
startups in certain promising sectors;
– Development of a specific tax regime for innovative
digital companies;
– Development of a regulatory framework relating to the establishment and
management of digital companies;
– Development of coordination procedures for financial partners;
– Encourage the development of distance training accessible on the
Internet;
– Raise the awareness of government and business officials
about the use of social networks;
– Carry out the legal and regulatory audit of the legal framework;
– Audit and evaluate programs and projects in the sector;
– Regulate the activities of ICT service providers (application developers, supplies of consumables, etc.) and define a reference
system for quality assurance and certification of products and companies;
– Establish a regulatory framework conducive to the development of alternative telecommunications operators, particularly in the field of value-added services.
PRIORITY ACTION PLAN FOR
THE DIGITAL ECONOMY
IN CAMEROON
Digital Cameroon 2020 Strategic Plan 41
42
Strategic Axis 1: DEVELOP BROADBAND INFRASTRUCTURES
Digital Cameroon 2020 Strategic Plan PRIORITY
ACTION PLAN Strategic Objective: Generalize broadband access for citizens , businesses and households
43
Strategic Axis 1: DEVELOP BROADBAND INFRASTRUCTURE
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 PRIORITY
ACTION PLAN
44
Strategic Axis 1: DEVELOP BROADBAND INFRASTRUCTURE
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 PRIORITY
ACTION PLAN
45
Strategic Axis 2: INCREASE THE PRODUCTION AND OFFER OF DIGITAL CONTENT
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 PRIORITY
ACTION PLAN Strategic Objective: To have attractive content developed, hosted and used at the local level.
46
Strategic Axis 2: INCREASE THE PRODUCTION AND OFFER OF DIGITAL CONTENT
Cameroon Digital 2020 Strategic Plan PRIORITY
ACTION PLAN
47
Strategic Axis 3: ENSURE THE DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION
OF ADMINISTRATION AND COMPANIES
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 PRIORITY
ACTION PLAN Strategic Objective: Accelerate the digital transformation of administration and companies to increase their efficiency, transparency, competitiveness and productivity
48
Strategic Axis 3: ENSURING THE DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION
OF ADMINISTRATION AND BUSINESS
Digital Cameroon 2020 Strategic Plan PRIORITY
ACTION PLAN
49
Strategic Axis 3: ENSURE THE DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION
OF THE ADMINISTRATION AND BUSINESS
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 PRIORITY
ACTION PLAN
50
Strategic Axis 3: ENSURE THE DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION
OF ADMINISTRATION AND BUSINESS
Digital Cameroon 2020 Strategic Plan PRIORITY
ACTION PLAN
51
Strategic Axis 4: PROMOTE DIGITAL CULTURE BY
GENERALIZING THE USE OF ICT IN SOCIETY
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 PRIORITY
ACTION PLAN Strategic Objective: Improve the quality of life of citizens through better use of digital technology.
52
Strategic Axis 5: STRENGTHENING DIGITAL CONFIDENCE
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 PRIORITY
ACTION PLAN Strategic Objective: Establish favorable conditions to create confidence in the digital economy.
53
Strategic Axis 5: STRENGTHENING DIGITAL CONFIDENCE
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 PRIORITY
ACTION PLAN
54
Strategic Axis 5: STRENGTHENING DIGITAL CONFIDENCE
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 PRIORITY
ACTION PLAN
55
Strategic Axis 5: STRENGTHENING DIGITAL CONFIDENCE
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 PRIORITY
ACTION PLAN
56
Strategic Axis 6: DEVELOP A LOCAL DIGITAL INDUSTRY
AND ENCOURAGE RESEARCH AND INNOVATION
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 PRIORITY
ACTION PLAN Strategic Objective: Provide locally produced digital goods and services at the national level.
57
Strategic Axis 6: DEVELOP A LOCAL DIGITAL INDUSTRY
AND ENCOURAGE RESEARCH AND INNOVATION
Digital Cameroon 2020 strategic plan PRIORITY
ACTION PLAN
58
Strategic Axis 6: DEVELOP A LOCAL DIGITAL INDUSTRY
AND ENCOURAGE RESEARCH AND INNOVATION
Digital Cameroon 2020 strategic plan PRIORITY
ACTION PLAN
59
Strategic Axis 7: ENSURE THE DEVELOPMENT OF HUMAN CAPITAL
AND LEADERSHIP IN DIGITAL
Cameroon Digital Strategic Plan 2020 PRIORITY
ACTION PLAN Strategic Objective: Ensure the availability in quality and quantity of human skills able to meet the needs of the Digital Economy.
60
Strategic Axis 7: ENSURE THE DEVELOPMENT OF HUMAN CAPITAL
AND LEADERSHIP IN DIGITAL
Cameroon Digital Strategic Plan 2020 PRIORITY
ACTION PLAN
61
Strategic Axis 7: ENSURE THE DEVELOPMENT OF HUMAN CAPITAL
AND LEADERSHIP IN DIGITAL
Cameroon Digital Strategic Plan 2020 PRIORITY
ACTION PLAN
62
Axis 8: ENSURE THE IMPROVEMENT OF GOVERNANCE
AND INSTITUTIONAL SUPPORT
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 PRIORITY
ACTION PLAN Strategic Objective: Create an environment conducive to the development of digital technology for economic development.
63
Axis 8: ENSURE THE IMPROVEMENT OF GOVERNANCE
AND INSTITUTIONAL SUPPORT
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 PRIORITY
ACTION PLAN
64
Axis 8: ENSURE THE IMPROVEMENT OF GOVERNANCE
AND INSTITUTIONAL SUPPORT
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 PRIORITY
ACTION PLAN
65
Axis 8: ENSURE THE IMPROVEMENT OF GOVERNANCE
AND INSTITUTIONAL SUPPORT
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 PRIORITY
ACTION PLAN
MECHANISM FOR IMPLEMENTATION
AND MONITORING-EVALUATION OF
THE STRATEGY
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 66
A- Implementation mechanism
The implementation of the strategic plan for the development of
the digital economy requires the efficient participation of the
various stakeholders, namely MINPOSTEL, public administrations, the private sector, civil society and
development partners. The implementing bodies
are summarized in the table below:
1- Strategic plan monitoring and evaluation mechanism
1.1. Monitoring and evaluation
Monitoring the implementation of the strategic plan for the development of the digital economy is particularly important. Thus, it will be carried out through a continuous process of
systematic collection of information, according to selected indicators
, to provide managers and stakeholders
with elements on the progress made, the objectives achieved and
the use of the allocated funds. In addition, it will ensure
that the planned programs and projects are running normally, and will improve their efficiency and effectiveness, if
necessary. Finally, monitoring will provide the opportunity to identify the
constraints to the implementation of programs and actions,
and to provide solutions.
The evaluation will consist of a systematic and objective assessment of the programs identified in the priority action plan, whether they are at the design or
implementation stage. Indeed, its objective will be to determine
the relevance and achievement of objectives,
development efficiency, effectiveness, impact and sustainability.
Consequently, the evaluation will focus both on the state
of progress of the implementation of the programs and on
the estimation of outputs, effects and impacts. It will be part of both
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 67
IMPLEMENTATION AND
MONITORING- EVALUATION
Ministry of Posts and
Telecommunications
(MINPOSTEL)
Administrations and bodies under the supervision of
MINPOSTEL
Private sector
Civil society
Development partners
Technical departments linking the
actions to be carried out
All Ministries, ANTIC, ART, CAMTEL,
ENSPT…
Start-ups, telephone companies, equipment manufacturers, ISP…
NGOs, GIC AND various ASSOCIATIONS…
ITU, UNDP, CEA, CEMAC, ECCAS,
WORLD BANK, ADB, EXIM-BANK
CHINA,… ASPECTS TOOLS OR IMPLEMENTATION
BODIES Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 68 IMPLEMENTATION AND MONITORING-EVALUATION in a short-term perspective than in the medium. Four
types of evaluation will be carried out, namely:
– ex-ante or a priori evaluation: this will take place when the programs and projects are designed and will focus
on the relevance and coherence of the projects in relation to
the desired aims and effects on the one hand, and to the development context
described by the 2035 vision and the DSCE on the other
hand. It will ensure the feasibility of the project and the existence
of operational objectives that can be monitored;
– the intermediate or mid-term evaluation: this will take place during the implementation, approximately halfway through the
life cycle of the project. At this level, it will be a question of
highlighting any discrepancies between the actual implementation
and initial goals. The conclusions of this evaluation
must lead to possible corrections, either in the management or in the very objectives of the project;
– the concomitant or on-going evaluation: it will be carried out
throughout the course of the implementation of the project
and consists of the continuous analysis of the state of progress of the
project, the context, the achievements made and the results
acquired ;
– ex-post or a posteriori evaluation: this will be carried out some
time after the end of the project and will report on the effects
observed and the overall impact.
The monitoring/evaluation tools that will be used are:
• project documents;
• progress reports;
• the surveys ;
• logistics, etc.
In addition, the monitoring of the implementation of the strategy should
be based on the following normative framework for monitoring and evaluation:
A clear logical framework for the digital domain: the objectives targeted, the activities/actions defined, the achievements expected, expected results and impacts;
A clear division of roles: this will make it possible to remove
overlapping responsibilities, facilitate
control operations and extend the practice of monitoring/evaluation (SE) at
all levels;
Qualified and sufficient
human resources and adequate financial resources allocated to monitoring/evaluation;
A clear and shared methodology: monitoring and evaluation of
the strategic plan will be systematic and objective. It will be carried out in a methodical, logical and coherent way
on the basis of predetermined criteria, to be viable;
Effective implementation: the periodicity and relevance
of the reports produced will be ensured;
Use of the conclusions and recommendations: this
will determine the relevance, timeliness and effectiveness of the monitoring-
evaluation.
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 69
IMPLEMENTATION AND
MONITORING-EVALUATION
1.2. Steering system for monitoring the implementation of
the strategic plan
At the political level: the various actors will take decisions with a view to improving the execution of the programs and projects of the priority action plan of the strategic plan. These
decisions are proposed by the PPBS Committees of each administration. In addition, at the beginning of each year, they validate
the orientations, the specifications, the work plan and the
timetable relating to the implementation of the strategic plan
, defined by the PPBS Committees.
At the strategic level: the monitoring of the implementation and the evaluation of the strategy are ensured by the PPBS Committees of the
various administrations concerned.
At the operational level: the monitoring of the implementation and the evaluation of the strategy are ensured by the Monitoring Units –
Evaluation (CSE) of PPBS Committees.
Their role also consists in defining the orientations, the specifications
, a work plan and a timetable of activities to be carried out during the budget year, for the monitoring and
evaluation of the actions provided for in the strategic plan. The
PPBS Committees also ensure the facilitation and development
of the synergies necessary for the efficient implementation of
the strategy, in particular through arbitration on issues submitted to it for examination and the taking of binding decisions by the permanent technical secretariat.
Following the implementation of the adopted strategic plan,
a measurement of the socio-economic impact of the recommended actions will be considered through the MINPOSTEL-INS partnership
whose agreement was signed on January 14, 2016 and which will
allow the measurement of ICT indicators and the analysis of gaps.
Digital Cameroon Strategic Plan 2020 70
GLOSSARY/
ABBREVIATIONS
A A
CE: Africa Coast to Europe submarine cable system
ANTIC: National Agency for Information and
Communication
Technologies APECCAM: Association of Professionals of Credit Institutions
in Cameroon
ART: Regulatory Agency for Telecommunications
B B
AD: African Development
Bank BEAC: Bank of Central African States
C C
AB: Central Africa Backbone
CAMPOST: Cameroon Postal Services
CAMTEL: Cameroon Telecommunications
CBSC: Cameroon to Brazil submarine cable system
CDMA: Code Division Multiple Access
CEA: Economic Commission for Africa (United Nations)
CEMAC: Economic and Monetary Community of Central Africa
CERT: Computer Emergency Response Team
CIIEJ: Integrated Center Information for Youth Entrepreneurship
CIRT: Computer Incident Response Team
CNPS: National Social Insurance Fund
CSE: Monitoring and Evaluation Units
D D
GSN: General Delegation for National Security
DSCE: Strategy Document for Growth and Employment
E E
GDI: E-Government Development Index
ENS: Ecole Normale Supérieure
ENSET: Ecole Normale Supérieure de l’Enseignement Technique
ENT: Digital Work Environment
F F
TTX: Fiber To The X (X= sidewalk, building, etc.)
GG
CI: Global Cybersecurity Index
GIC: Common Initiative Group
I I
XP: Internet Exchange Point
IPBX or PABX-IP: Private Automatic Branch eXchange – Internet Protocol
ISRC: International Standard Recording Code
N N
RI: Networked Readiness Index
M M
INAC: Ministry of Arts and Culture
MINADER: Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development
MINATD: Ministry of Territorial Administration and Decentralization
MINCOMMERCE: Ministry of Commerce
MINCOM: Ministry of Communication
MINEDUB: Ministry of Basic Education
MINEE: Ministry of Water and Energy
LocalHost Digital : Your Web & Digital Agency in Africa

The N°1 Digital Transformation Agency LocalHost Digital is at your disposal for all your projects. Our Digital Agency specializes in the Development and Integration of Digital Solutions for Companies (ERP, CRM, Commercial Management, Dedicated Solutions, etc.), the Creation of Professional Websites , the Development of Web and Mobile Applications , the Development of Business applications, Digital Marketing , as well as in Graphic Design and Practical Training in the various Digital professions . We are a Digital Transformation Company which stands out for its wide range of services and creative strategies, but above all for the quality of our achievements. We support and educate our customers so that they get the most out of the solutions we build with them.
We publish and integrate software solutions designed to simplify and optimize the management of specific businesses and activities:
- Business Management Software
- Stock Management Software / Warehouses
- School Management Software
- Hospital Management Software
- Hotel and Hostel Management Software
- Law Firm Management Software
- Sewing Salon Management Software
- Call Center Management Software
- Freight Business Management Software
- Whatsapp Bulk Messaging Software
- Restaurant Management Software
- Fleet Management Software
- ERP/CRM/HR/Project Management Software
- Medical Analysis Laboratories Management Software

Durrell NGOUANET DONGMO | Promoter of LocalHost Digital
Durrell NGOUANET is a young Engineer graduated from the National Polytechnic School of Yaoundé. Passionate about Digital Transformation and Specialist in Digital Solutions, He is attracted by the challenge and the resolution of business problems | An entrepreneur focused on the future, he is the Founder of the company LocalHost Group SARL and of the Training Center for Digital Professions LocalHost Academy | He is also the Founder of the Professional Social Network TheStarterbook , the Durrell Market e-commerce platform and many other digital initiatives.
Take advantage of the promotion to launch your professional website
We are specialists in the Creation of Professional Websites with several years of experience serving companies and individuals around the world. Consult our achievements by CLICKING HERE
Some Recent Achievements of LocalHost Digital: Best Web and Digital Agency in Cameroon
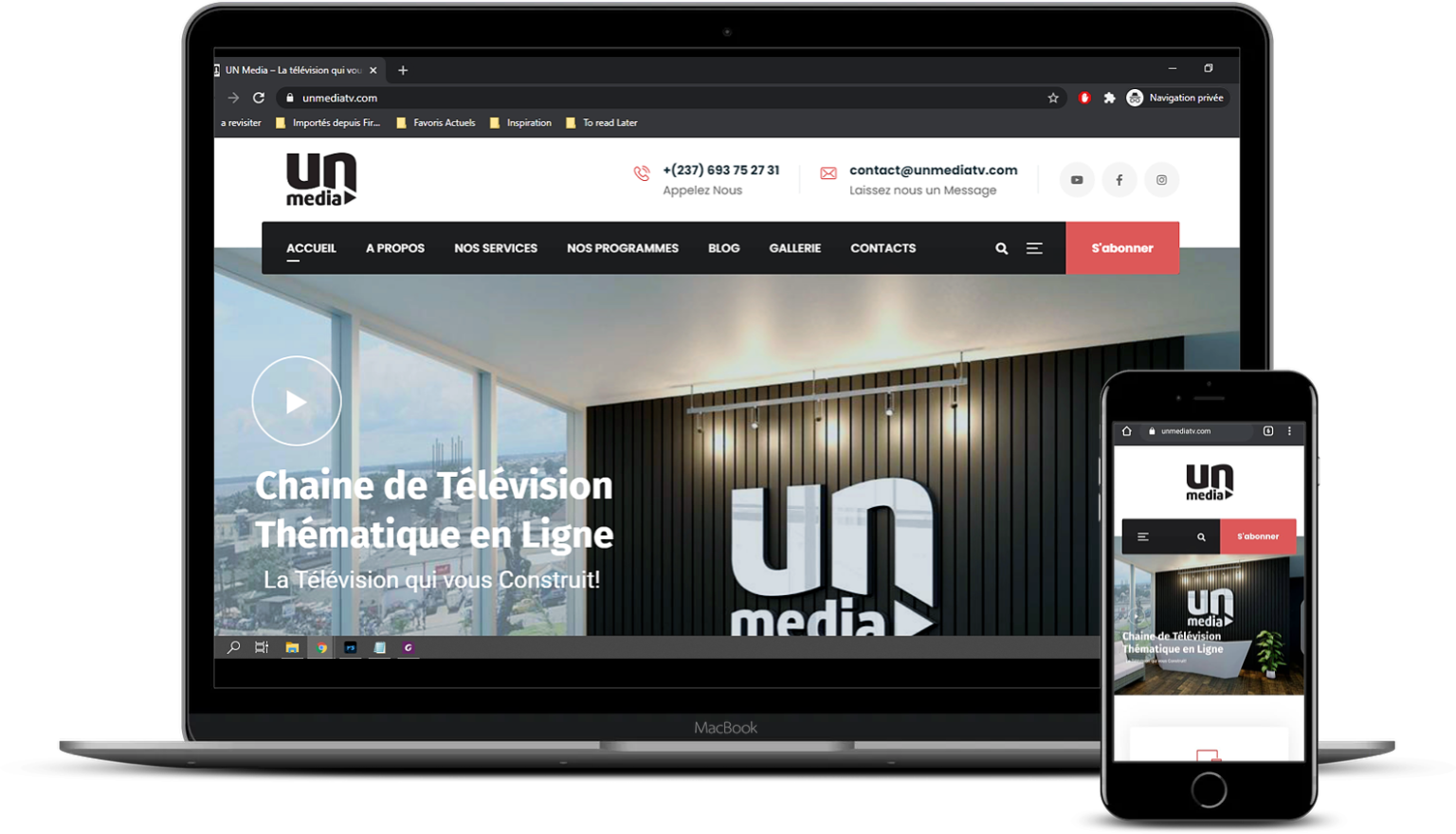
LocalHost Digital for the company UN Media
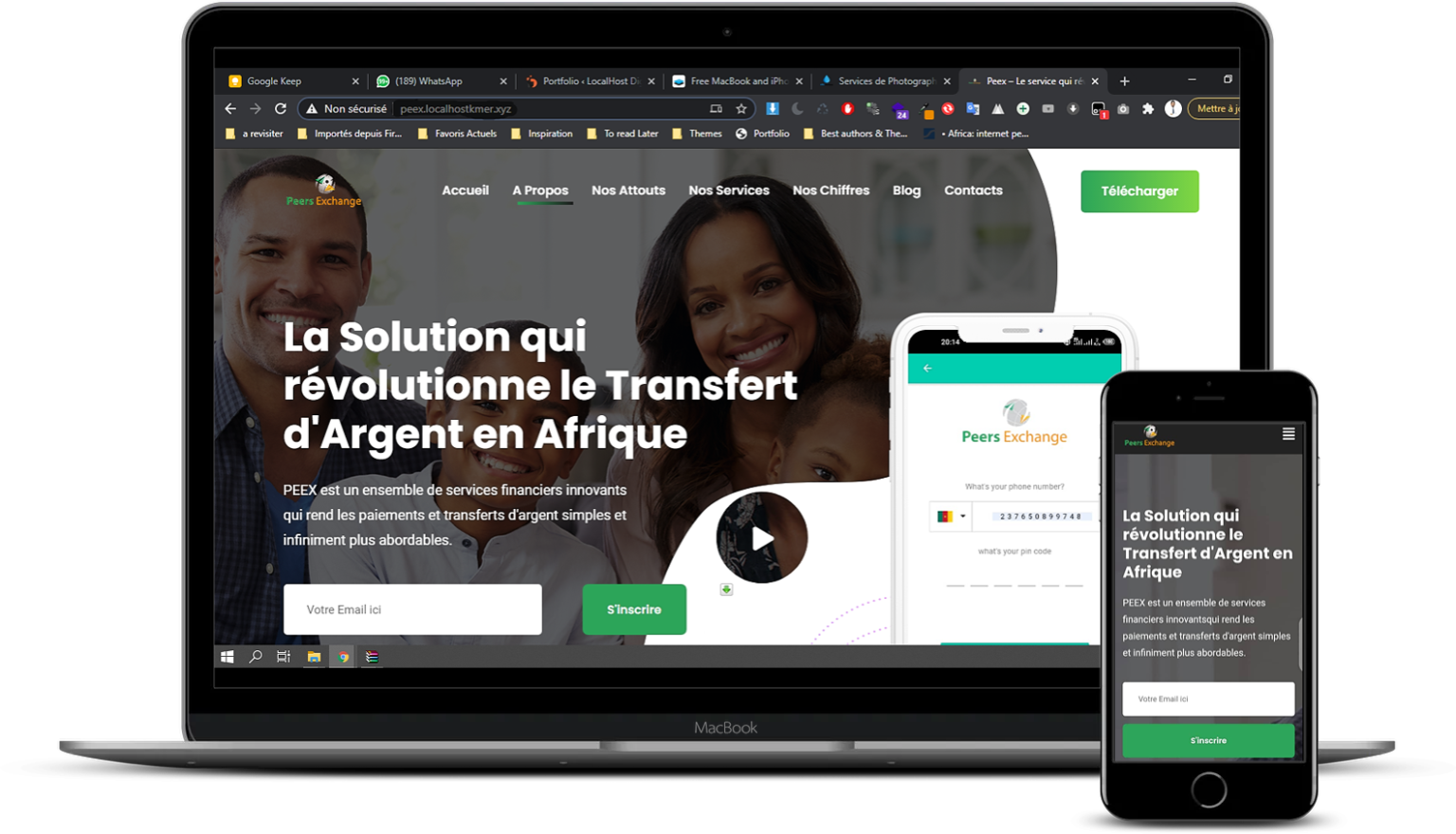
LocalHost Digital for the company PeexPay based in France
LocalHost Digital for L’institut d’Art Oratoire
LocalHost Digital for the company Ever Connect based in Ivory Coast
LocalHost Digital for the company Hachther, Online Payment Solution

LocalHost Digital for Gab’s Shop

LocalHost Digital for the company KTK Deals SARL
LocalHost Digital for the company Alibase based in Chad

LocalHost Digital for the company IDOLE
0